Understanding Web Hosting: A Beginner's Guide
-

- Web Hosting
- Jan 19, 2024
-
0views
- Reading time: 13 minutes

Embarking on the journey of creating your own website is an exciting endeavor, but before you can launch your online presence, it's crucial to understand the backbone of every successful website—web hosting. In this beginner's guide, we'll unravel the mysteries of web hosting, breaking down the key concepts, types of hosting, and what factors to consider when choosing the right hosting provider for your needs.
Section 1: What is Web Hosting?
Creating a website involves more than just designing a visually appealing interface or crafting engaging content. At its core, web hosting is the engine that makes your website accessible to the world. Let's delve deeper into the essential components of web hosting and demystify the terminology.
-
Server: The Digital Landlord: At the heart of web hosting is the server. Think of a server as a powerful computer with ample storage and processing capabilities. When users access your website, they are essentially connecting to this server, which houses all the files, databases, and resources needed to display your site.
Servers can be physical machines located in data centers or virtual instances in the cloud. The choice between physical and virtual servers depends on factors like scalability, maintenance, and resource requirements.
See our server options here -
Bandwidth: The Information Highway: Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transferred between your server and visitors to your website. It determines how fast and efficiently your website can load for users. If your website is analogous to a house, bandwidth is the width of the road leading to it—the broader the road (higher bandwidth), the smoother the traffic (faster loading times).
Understanding bandwidth is crucial because exceeding allocated bandwidth limits can lead to slower website performance or even temporary unavailability.
-
Storage: Your Digital Closet: Websites consist of various files, including images, videos, scripts, and databases. These files need a place to reside, and that place is the storage space on your server. Storage is like a digital closet where you keep all the assets that make up your website.
Different hosting plans offer varying amounts of storage, and it's essential to choose a plan that accommodates your website's size and future growth.
-
Domain Name: Your Digital Address: While not a direct component of web hosting, your domain name is closely associated. It serves as the human-readable address that users type into their browsers to access your website. The domain name acts as a pointer, directing visitors to the specific server where your website is hosted.
Registering a domain name is a separate process from acquiring hosting, but the two must be connected to make your website accessible under your chosen domain.
Understanding these fundamental elements of web hosting sets the stage for navigating the intricacies of hosting plans and providers. As you embark on your web hosting journey, envision your website as a digital residence, and the hosting infrastructure as the essential framework that brings it to life on the vast landscape of the internet.
Section 2: The Basic Components of Web Hosting:
Now that we have a foundational understanding of what web hosting is, let's delve deeper into the core components that shape the hosting experience. These components not only determine the technical aspects of your hosting but also play a pivotal role in the overall performance and reliability of your website.
-
Server Types:
-
Shared Servers: In shared hosting, multiple websites share resources on the same server. It's like living in an apartment building where residents share common spaces. This option is cost-effective and suitable for smaller websites with moderate traffic.
-
VPS (Virtual Private Server): VPS hosting offers a virtualized private space on a server. It provides more control and dedicated resources compared to shared hosting, making it an excellent choice for growing websites.
-
Dedicated Servers: With dedicated hosting, you have an entire server exclusively for your website. This is akin to owning a standalone house. Dedicated servers are ideal for large websites with high traffic and resource-intensive applications.
-
Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected servers. It offers scalability, flexibility, and reliability by drawing resources from multiple servers. Cloud hosting is suitable for websites expecting variable traffic levels.
-
-
Bandwidth and Data Transfer:
-
Bandwidth Allocation: Hosting plans come with a specified amount of bandwidth, dictating the volume of data that can be transferred between the server and visitors. Plans with higher bandwidth are essential for handling increased traffic and ensuring fast-loading pages.
-
Data Transfer: Some hosting providers may impose additional fees for exceeding allocated bandwidth. It's crucial to understand your website's data transfer needs and select a plan accordingly to prevent unexpected costs.
-
-
Storage Space:
-
Disk Space Allocation: The amount of storage space provided in a hosting plan determines how much data your website can store. Consider the size of your website files, databases, and any anticipated growth when choosing a hosting plan.
-
Solid State Drives (SSD): Hosting providers may offer SSDs, which are faster and more reliable than traditional hard disk drives (HDD). SSDs contribute to quicker data retrieval and faster website performance.
-
-
Uptime and Reliability:
-
Uptime Guarantees: Uptime refers to the time your website is accessible to users. Hosting providers often offer uptime guarantees as a percentage. For example, a 99.9% uptime guarantee means your website should be operational 99.9% of the time.
-
Redundancy and Backup Systems: Reliable hosting providers implement redundancy measures and backup systems to minimize downtime in case of server failures or other unforeseen events.
-
Understanding these components empowers you to make informed decisions when selecting a hosting plan. The right combination of server type, bandwidth, storage, and reliability features ensures that your website not only functions smoothly but can also accommodate future growth and fluctuations in traffic. As you embark on your web hosting journey, consider these elements as the building blocks of a robust online presence.
Section 3: Types of Web Hosting:
In the vast landscape of web hosting, different types of hosting cater to diverse needs, from personal blogs to large-scale e-commerce platforms. Understanding the various types of web hosting is crucial for choosing the right solution that aligns with your website's requirements and growth plans.
-
Shared Hosting:
-
Ideal for: Beginners, Small Websites, Low to Moderate Traffic
-
Shared hosting is akin to renting a room in an apartment complex where multiple tenants share the same resources (server). It's cost-effective and straightforward, making it an excellent starting point for those new to website hosting.
-
Pros:
- Cost-effective.
- User-friendly for beginners.
- Maintenance is handled by the hosting provider.
-
Cons:
- Limited resources shared among multiple websites.
- Performance may be impacted by neighboring sites.
- Less control compared to other hosting types.
-
-
Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting:
-
Ideal for: Growing Websites, Moderate to High Traffic
-
VPS hosting offers a dedicated virtual space on a shared server. It provides more control and resources than shared hosting, making it suitable for websites that have outgrown entry-level hosting.
-
Pros:
- More control and customization.
- Higher performance compared to shared hosting.
- Scalable to accommodate increased traffic.
-
Cons:
- Costs more than shared hosting.
- Technical knowledge may be required for configuration.
-
-
Dedicated Hosting:
-
Ideal for: High-Traffic Websites, Resource-Intensive Applications
-
With dedicated hosting, you have an entire server exclusively for your website. It's like owning a standalone house with full control over resources, making it suitable for large-scale websites and applications.
-
Pros:
- Maximum control and customization.
- High performance and reliability.
- Ideal for resource-intensive applications.
-
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to shared and VPS hosting.
- Requires technical expertise for server management.
-
-
Cloud Hosting:
-
Ideal for: Scalable Solutions, Variable Traffic
-
Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected servers to provide flexibility and scalability. Resources are drawn from multiple servers, ensuring reliability and performance even during traffic spikes.
-
Pros:
- Scalable resources based on demand.
- High uptime and reliability.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing models.
-
Cons:
- Costs can vary based on usage.
- Complexity may require technical understanding.
-
Choosing the right type of hosting depends on factors such as your website's size, anticipated traffic, and technical requirements. As you explore these hosting options, consider your current needs and future growth plans to make an informed decision that aligns with the goals of your online presence.
If you're not sure which server is best for your site, get in touch with our help team. We'll find the best solution for you. Just click here
Section 4: Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hosting Provider:
Selecting the right hosting provider is a critical decision that directly influences the performance, security, and overall success of your website. With numerous hosting providers available, it's essential to consider a range of factors to ensure that your chosen provider meets your specific needs.
-
Uptime and Reliability:
-
Uptime Guarantees: Look for a hosting provider that offers a high uptime guarantee, such as 99.9% or higher. This ensures that your website remains accessible to visitors consistently.
-
Server Redundancy: Inquire about the provider's measures for server redundancy. Reliable hosting services implement backup systems and redundant infrastructure to minimize downtime in the event of hardware failures or other issues.
-
-
Customer Support:
-
24/7 Support: Opt for a hosting provider that offers round-the-clock customer support. Technical issues can arise at any time, and having access to responsive support ensures prompt resolution.
-
Communication Channels: Evaluate the available communication channels for customer support, such as live chat, email, and phone. Ensure that the provider's support channels align with your preferences and requirements.
-
-
Scalability:
-
Room for Growth: Consider the scalability of the hosting provider's plans. Your website may experience growth over time, and a hosting plan that allows for easy upgrades ensures that your hosting can adapt to increased traffic and resource demands.
-
Additional Resources: Check if the hosting provider offers scalable resources such as additional CPU, RAM, or storage when needed. Scalability is vital for accommodating the evolving needs of your website.
-
-
Security Features:
-
SSL Certificates: Look for hosting providers that include SSL certificates in their plans. SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption is essential for securing data transmitted between your website and visitors.
-
Firewalls and Malware Protection: Inquire about the security measures in place, including firewalls and malware protection. A secure hosting environment protects your website and user data from potential threats.
-
Regular Backups: Choose a hosting provider that performs regular backups of your website data. In the event of data loss or website issues, backups are crucial for restoring your site to a previous state.
-
-
Cost and Pricing Structure:
-
Transparent Pricing: Examine the provider's pricing structure to ensure transparency. Be aware of any hidden fees or additional charges that may apply.
-
Renewal Rates: Consider the renewal rates for hosting plans, as some providers may offer attractive introductory rates that increase upon renewal.
-
Payment Plans: Evaluate the available payment plans, including monthly, annual, or longer-term commitments. Choose a plan that aligns with your budget and preferences.
-
-
User-Friendly Interface:
-
Control Panel: Assess the user interface provided by the hosting provider. A user-friendly control panel, such as cPanel or Plesk, simplifies the management of your website, domain, and hosting settings.
-
One-Click Installations: Look for hosting providers that offer one-click installations for popular content management systems (CMS) and applications. This makes it easier to set up and manage your website.
-
-
Reviews and Reputation:
-
Customer Reviews: Research customer reviews and testimonials to gain insights into the experiences of other users with the hosting provider. Look for reviews that highlight aspects such as customer support, reliability, and overall satisfaction.
-
Reputation in the Industry: Consider the provider's reputation in the hosting industry. Established and reputable hosting companies are more likely to offer reliable services and customer support.
-
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing a hosting provider that aligns with the unique requirements and goals of your website. Remember that selecting a reliable hosting partner is an investment in the long-term success and performance of your online presence.
Section 5: Setting Up Your Website:
Once you've chosen a suitable hosting provider and plan, the next step is to set up your website on the hosting platform. This involves linking your domain name to the hosting service, configuring essential settings, and ensuring a smooth launch. Let's explore the key steps in setting up your website.
-
Domain Registration:
-
Choose a Domain: If you haven't already registered a domain, choose a relevant and memorable domain name for your website. Consider using your business name or a name that reflects the purpose of your site.
-
Domain Extensions: Select a domain extension (e.g., .com, .net, .org) that suits your website. While .com is widely used, other extensions may be more fitting for specific purposes.
-
Domain Privacy Protection: Consider enabling domain privacy protection to keep your personal information private. This feature prevents your contact details from being publicly listed in the domain registration database.
-
-
Connecting Your Domain to Hosting:
-
Update DNS Settings: To connect your domain to the hosting provider, update the domain's DNS (Domain Name System) settings. This involves configuring the domain's nameservers to point to the hosting provider's nameservers.
-
Propagation Period: Keep in mind that DNS changes may take some time to propagate across the internet. This propagation period can range from a few hours to 48 hours. During this time, your website may not be accessible to all users.
-
-
Install a Content Management System (CMS):
-
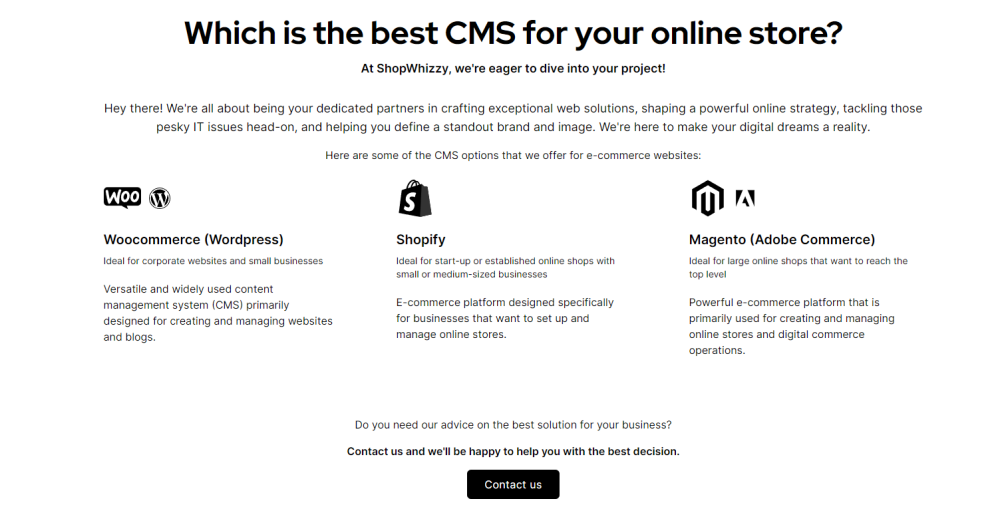
Select a CMS: Choose a content management system for your website. Popular options include WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal. Many hosting providers offer one-click installations for these CMS platforms.
-
One-Click Installation: Use the hosting provider's control panel to perform a one-click installation of your chosen CMS. This simplifies the setup process, allowing you to quickly establish the framework for your website.
-
-
Configure Website Settings:
-
General Settings: Configure general settings within your CMS, such as the site title, tagline, and default language. These settings provide basic information about your website.
-
Permalinks: Set up permalinks to define the structure of your website's URLs. Choose a format that is user-friendly and reflects the organization of your content.
-
-
Design and Customize:
-
Choose a Theme: Select a theme or template for your website that aligns with your brand and design preferences. Many CMS platforms offer a variety of free and premium themes.
-
Customization Options: Explore customization options within your CMS to personalize the appearance of your website. This may include adjusting colors, fonts, and layout settings.
-
-
Add Content:
-
Create Pages and Posts: Start adding content to your website by creating pages (e.g., Home, About Us, Contact) and posts (if applicable). Provide informative and engaging content that resonates with your audience.
-
Media Uploads: Upload images, videos, and other media files to enhance the visual appeal of your website. Optimize media files for web use to ensure faster page loading times.
-
-
Setup Essential Plugins:
-
Security Plugins: Install security plugins to enhance the security of your website. These plugins may offer features such as firewall protection, malware scanning, and login attempt monitoring.
-
SEO Plugins: Implement SEO (Search Engine Optimization) plugins to optimize your website for search engines. These plugins can help improve your site's visibility in search engine results.
-
-
Implement Regular Backups:
-
Backup Solutions: Set up a regular backup schedule for your website. Many hosting providers offer built-in backup solutions, and there are also plugins available for CMS platforms that facilitate automated backups.
-
Offsite Backups: Consider storing backups in an offsite location or using cloud-based backup services. This provides an additional layer of security in case of server issues.
-
-
Test Your Website:
-
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Test your website across different web browsers to ensure compatibility. Your website should display correctly and function seamlessly on popular browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
-
Mobile Responsiveness: Verify that your website is mobile-responsive. With a significant portion of internet users accessing websites via mobile devices, it's crucial that your site provides a positive experience on smartphones and tablets.
-
-
Launch Your Website:
-
Remove Under Construction Pages: If you had an under-construction or placeholder page, remove it once your website is ready to go live. This ensures that visitors can access the complete version of your site.
-
Announce Your Launch: If applicable, announce the launch of your website through social media, email newsletters, or other communication channels. Encourage friends, family, and colleagues to visit and provide feedback.
-
By following these steps, you'll successfully set up your website on your chosen hosting platform. Remember that the process may vary slightly depending on your CMS and hosting provider, so consult their documentation or support resources for specific guidance. With your website live, you've officially joined the online realm, ready to share your content, products, or services with the world.
Conclusion
Understanding web hosting is a crucial step in establishing a successful online presence. With this beginner's guide, you should now have a solid grasp of the fundamental concepts, types of hosting, and key considerations when choosing a hosting provider. As you embark on your web hosting journey, remember that selecting the right hosting solution lays the foundation for a secure, reliable, and efficient website. Happy hosting!